call 800-291-1732 (Who Answers?) for a free referral.
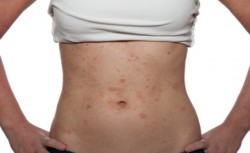
There are symptoms that can be caused due to Codeine allergies.
Codeine is a commonly prescribed pain medication that is used to treat mild to moderate acute pain and can also be used to treat cough. Although rare, codeine allergies do occur and can lead to some dangerous symptoms. Typically, a codeine allergy will not occur with the initial or first exposure of the drug but will most often take place with a subsequent exposure. Often times, codeine allergies are somewhat genetic in scope meaning that if your parents or grandparents are allergic to codeine, you are likely to be allergic to the drug as well.
It is important to recognize that the symptoms of an allergic reaction to codeine are quite different than those related to the general side-effects of the drug. Many people, especially those who do not regularly take pain medications, mistakenly think that the side-effects of codeine such as nausea and vomiting, are actually symptoms of an allergic reaction but in most cases, this is untrue.
Symptoms of an Allergic Reaction to Codeine
Allergic reactions can come on quickly and must be treated quickly to ensure the safety of the patient.
The most common symptoms of an allergic reaction to codeine include:
- Hives
- Swelling of the lips, tongue or throat
- Itching that is severe or cannot be stopped
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Dizziness
Reversing an Allergic Reaction
If you experience symptoms of an allergic reaction after taking a dose of codeine, immediate medical help is recommended to ensure your safety. Swelling of the lips, throat, or tongue or having difficulty breathing are signs of a serious allergic reaction that should be treated promptly with emergency medical care. Epinephrine is often effective at reversing the allergic reaction.
For mild allergic reactions to codeine, replacing the medication with another effective pain medicine is often a suitable method of reducing the risk of additional symptoms from occurring. If allergy symptoms are mild and do not include difficulty breathing or swelling in the face, lips or tongue, discontinue use of the drug and consult your physician for an alternative medication. Your doctor may recommend you take another pain medication such as Demerol for the treatment of pain.

 History of Codeine -
Opiates have been used throughout history for hundreds of years dating as far back as the Egyptians and the Ancient Chinese and their use of opium. Codeine itself dates back to the 19th century when opium was first used in various proportions along with other drugs to create various forms of opioids. Codeine is found ...
History of Codeine -
Opiates have been used throughout history for hundreds of years dating as far back as the Egyptians and the Ancient Chinese and their use of opium. Codeine itself dates back to the 19th century when opium was first used in various proportions along with other drugs to create various forms of opioids. Codeine is found ...  Why Codeine is a Popular Choice Among Addicts -
Codeine is often found in cough syrup and is less regulated than other opiate-based drugs, making it seem like a safer option.
Why Codeine is a Popular Choice Among Addicts -
Codeine is often found in cough syrup and is less regulated than other opiate-based drugs, making it seem like a safer option.  Accepted Medical Codeine Uses -
Codeine serves a wide variety of uses as a pain relief medication. According to the U. S. Food & Drug Administration, as a narcotic opiate drug, codeine works well as a treatment for mild, moderate and severe pain symptoms. It’s also an active ingredient in many over-the-counter cough suppressant drugs. This wide range of medical ...
Accepted Medical Codeine Uses -
Codeine serves a wide variety of uses as a pain relief medication. According to the U. S. Food & Drug Administration, as a narcotic opiate drug, codeine works well as a treatment for mild, moderate and severe pain symptoms. It’s also an active ingredient in many over-the-counter cough suppressant drugs. This wide range of medical ...  Brand Names -
Codeine is most often combined with other medications and then marketed under certain brand names such as Robitussin AC which contains codeine. There are many branded products on the market that include a combination of codeine and another drug such as Phenylephrine, Pyrilamine, Guaifenesin or Chlorpheniramine. Other combination products may also be found in the medical field ...
Brand Names -
Codeine is most often combined with other medications and then marketed under certain brand names such as Robitussin AC which contains codeine. There are many branded products on the market that include a combination of codeine and another drug such as Phenylephrine, Pyrilamine, Guaifenesin or Chlorpheniramine. Other combination products may also be found in the medical field ...  What is Codeine? -
Codeine is a member of the opioid family of drugs that is derived from the opium poppy and synthesized in a laboratory to create an analgesic drug that is common prescribed for the treatment of mild to moderate pain, cough and sometimes diarrhea. Codeine is considered a narcotic and it does carry a potential for ...
What is Codeine? -
Codeine is a member of the opioid family of drugs that is derived from the opium poppy and synthesized in a laboratory to create an analgesic drug that is common prescribed for the treatment of mild to moderate pain, cough and sometimes diarrhea. Codeine is considered a narcotic and it does carry a potential for ...